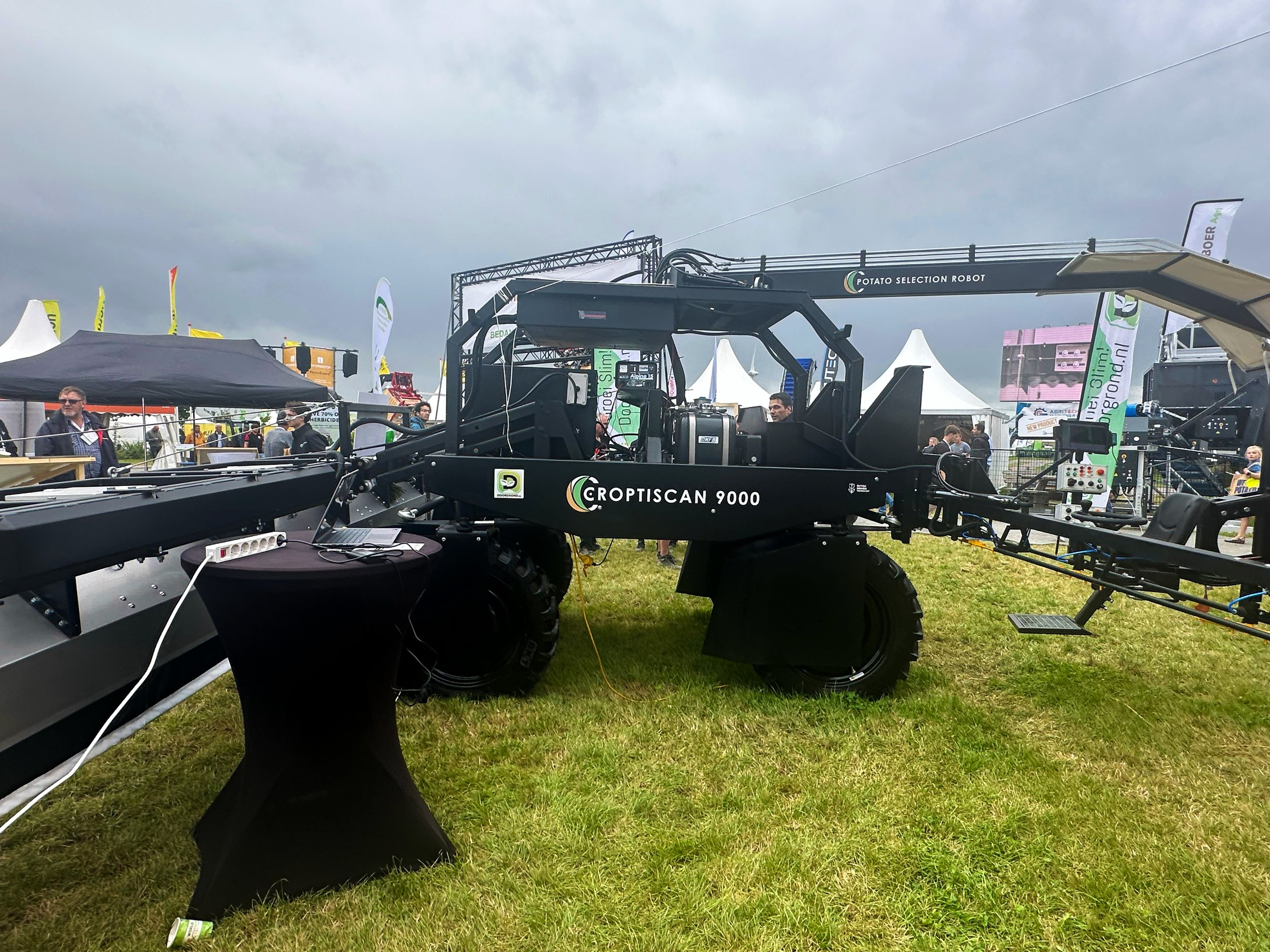
Ag-tech: Speed and accuracy with seed sensing technology
New seed sensing tech helps pinpoint missed or doubled seeds in real time—boosting accuracy and yield while cutting waste. Read more to learn about developments in ag-tech in the potato industry.
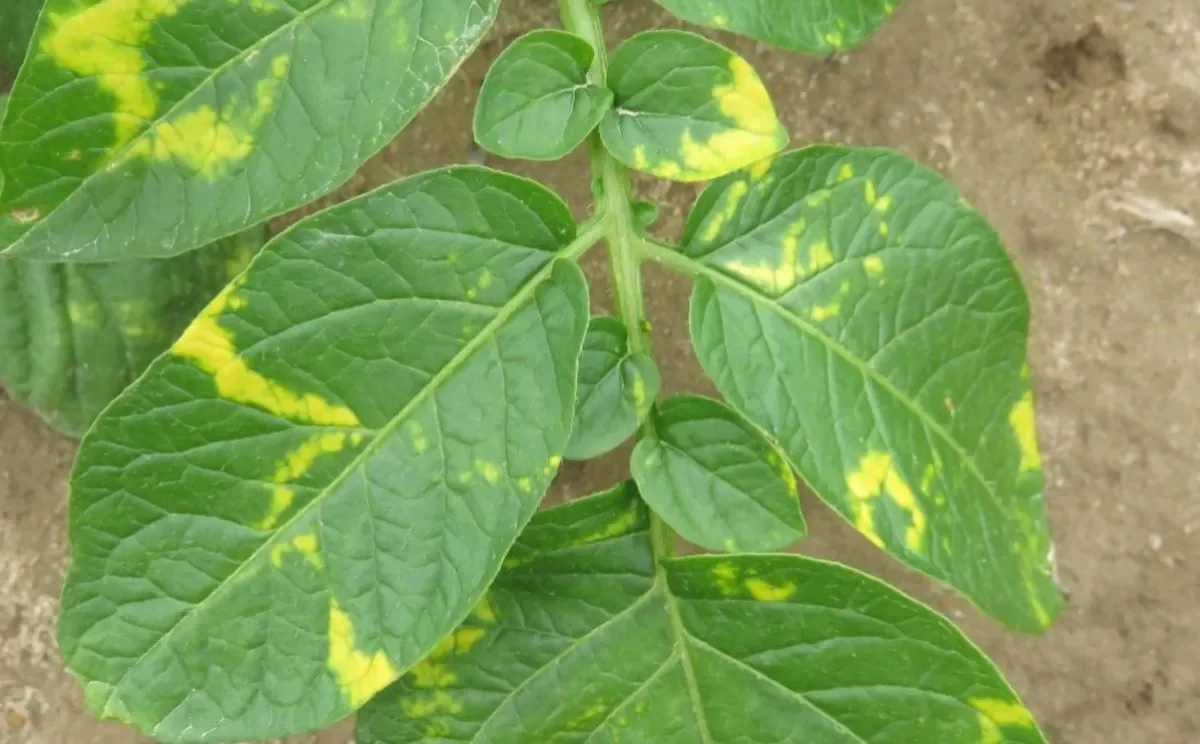
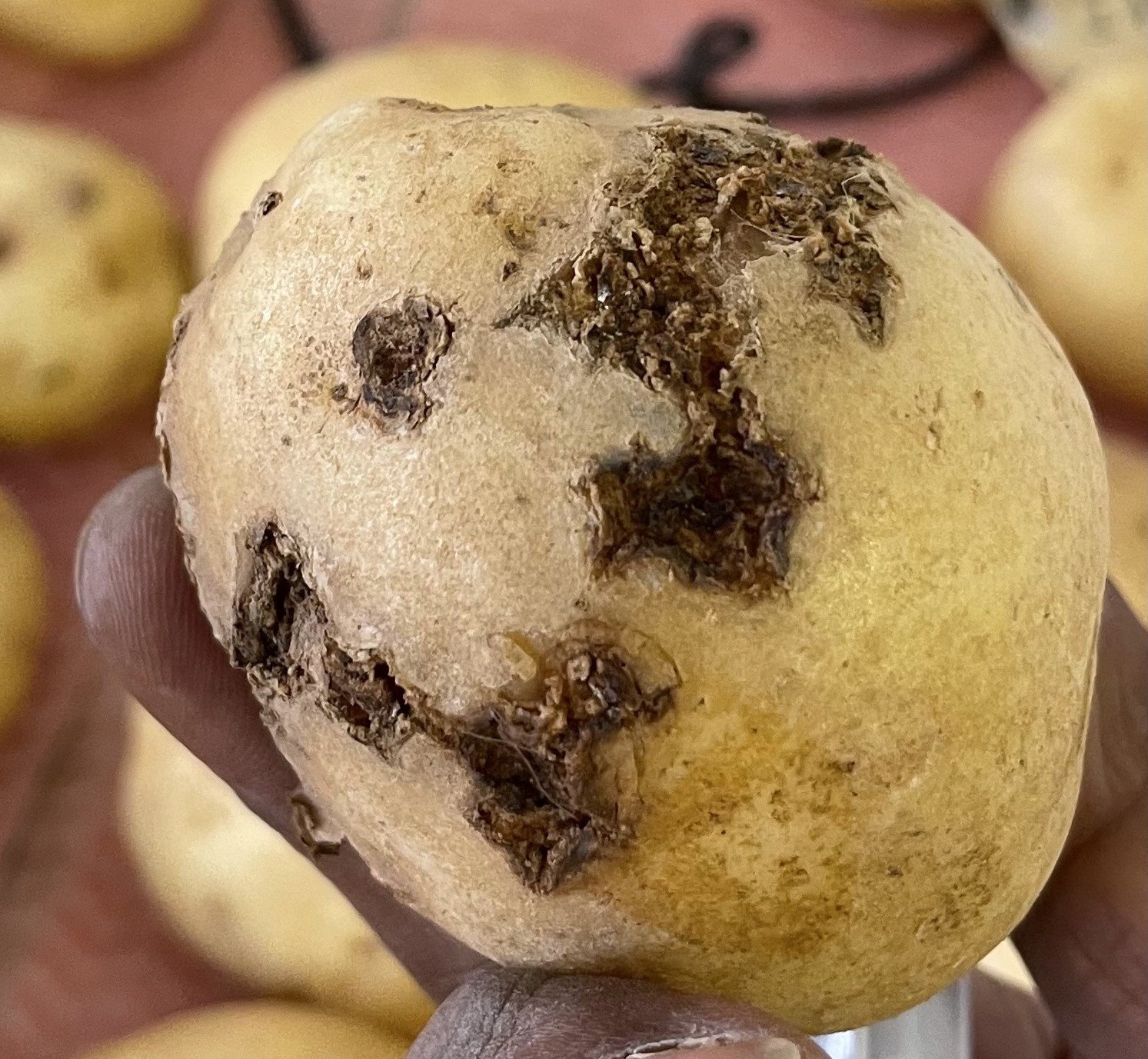
Monitoring key soil-borne diseases of fresh potato in WA
A WA study used DNA-based tools to track powdery scab, black dot, and common scab. The findings highlight both the value and limits of soil testing in managing the impact of disease on tuber quality and yield. Read more in Issue 16 of PotatoLink magazine.
Ask the Spud GP: N and early blight
Can extra nitrogen protect potatoes from early blight? The Spud GP article from Issue 16 of PotatoLink magazine answers a grower’s question, sharing the latest research on when and how to apply nitrogen for the best disease resistance.